- Soins généraux
- Médecine générale
- NeoSys Medical Solutions
- Société
- Produits
- Catalogues
- News & Trends
- Salons
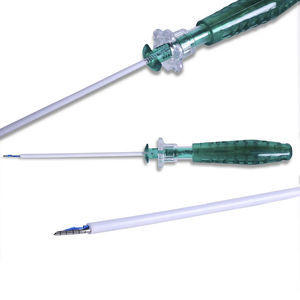
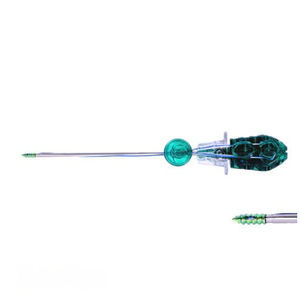
Garrot ischémique élastique NEO-Tchirurgicaljetable
Ajouter à mes favoris
Ajouter au comparateur
Vous voulez acheter directement ?
Rendez-vous sur notre Shop.
Caractéristiques
- Type
- élastique
- Applications
- chirurgical
- Autres caractéristiques
- jetable
Description
Bloodless, dry surgical fieldAvoids risks of incomplete exsanguinationImproved anatomical visibilityReduced incidence of post-op DVTReduced incidence of pulmonary embolismReduces blood loss, resulting in decreased need for blood transfusionSTERILITYReduced risk of Surgical Site Infection (SSI)Single-useNARROW CUFFIncreased visibilityIncreased accessibilityLess likelihood of side effects due to pressure on tissueEFFICIENCYReduced patient preparation time – 15 seconds vs. 12 minutesReduced OR clutterQuick & easy to applyProduct OverviewNEO-T is a Sterile Surgical Tourniquet. It is an innovative all-in-one device that combines three important functions:Superior exsanguinationA large sterile surgical fieldBlocking of arterial blood re-entryDeficiencies of Existing SolutionsMAXIMAL EXSANGUINATION IS NEEDED TO PREVENT PULMONARY & CEREBRAL EMBOLIZATION.Partial exsanguination is inherent in the traditional Esmarch/Pneumatic Tourniquet method.RISKS OF INCOMPLETE EXSANGUINATION (<67%):Pulmonary Emboli (PE): Blood left behind results in clots and intravascular clotting and often occurs during surgery where a tourniquet is used. When the tourniquet is deflated, blood clots migrate to the heart and lungs, leading to risk of brain infarcts, e.g. post TKA Cognitive Dysfunction. Near perfect exsanguination by NEO-T largely prevents embolization.Cerebral Emboli & Infarction: Small emboli block small arteries, reducing or preventing blood flow to brain regions, followed by small infarctions, resulting mostly in cognitive dysfunction. (*Thromboembolism Coincident with Tourniquet Deflation During Total Knee Arthroplasty. Lancet. 1993 Apr 24;341(8852):1057-8)Post operative side effects: Risk of post-op DVT, skin injury, tourniquet burn (20.7%), tourniquet pain (39.7%), and nerve damage.STERILITY ISSUES: Increased risk of Surgical Site Infection (SSI). Non-Sterile Pneumatic Tourniquets are Contaminated. A Potential Cause of SSI. Sterile NEO-T is 100% safe.REDUCED ACCESSIBILITY – WIDE CUFF: Reduced access, especially in obese limb or pediatric cases and limited anatomical visibility during surgerySIDE EFFECTS DUE TO PRESSURE ON TISSUES: Traditional wide cuffs produce increased uniform pressure inside the limb vs. the NEO-T narrow cuff where axial and radial pressure gradients result in less force on inner tissue.INEFFICIENCIES: Increased preparation and setup time, less procedures, high cost derivative, and OR clutter.Time wasted: Traditional methods require 12 minutes of patient setup time vs. 15 seconds with NEO-T applicationInefficiency and aggregate cost of multiple products used during a procedure that employs the pneumatic tourniquet vs. the single-use sterile NEO-T device.OR clutter and shelf space incurred by the pneumatic tourniquet method is eliminated by NEO-TTechnical Specifications / Features:Sterile, single-use surgical tourniquetNarrow cuff for increased visibility and accessibilityReduces risk of SSI, DVT, pulmonary embolism, and nerve damageQuick application (15 seconds)All-in-one device: exsanguination, surgical field, arterial blockReduces blood loss and need for transfusionMinimizes OR clutter and preparation time
Catalogues
Aucun catalogue n’est disponible pour ce produit.
Voir tous les catalogues de NeoSys Medical SolutionsAutres produits NeoSys Medical Solutions
KNEE-ANKLE-SMALL JOINT
* Les prix s'entendent hors taxe, hors frais de livraison, hors droits de douane, et ne comprennent pas l'ensemble des coûts supplémentaires liés aux options d'installation ou de mise en service. Les prix sont donnés à titre indicatif et peuvent évoluer en fonction des pays, des cours des matières premières et des taux de change.